Class-imbalanced Time Series Adaptation via Multi-Expert Consistency Entropy Minimization
Published in IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, 2024
Wearable-based time series recognition aims to infer behavioral classes based on time series signals collected by sensors. Domain Adaptation (DA) methods have significantly improved the performance on out-of-domain test classification tasks. However, highly imbalanced label distribution in real-world tasks hinders the practicality of DA methods.
The performance is contingent on the extent of label imbalance. With an escalating imbalance in label distribution, decision boundaries become increasingly skewed toward minority classes. Consequently, committee methods demonstrate a bias towards majority classes, leading to diminished applicability. Moreover, basic augment transformations for time series classification, as opposed to image classification, may introduce alterations in semantics. To effectively handle time series data in a specific classification task, it is essential to have a sufficiently extensive range of semantically invariant augmented spaces.
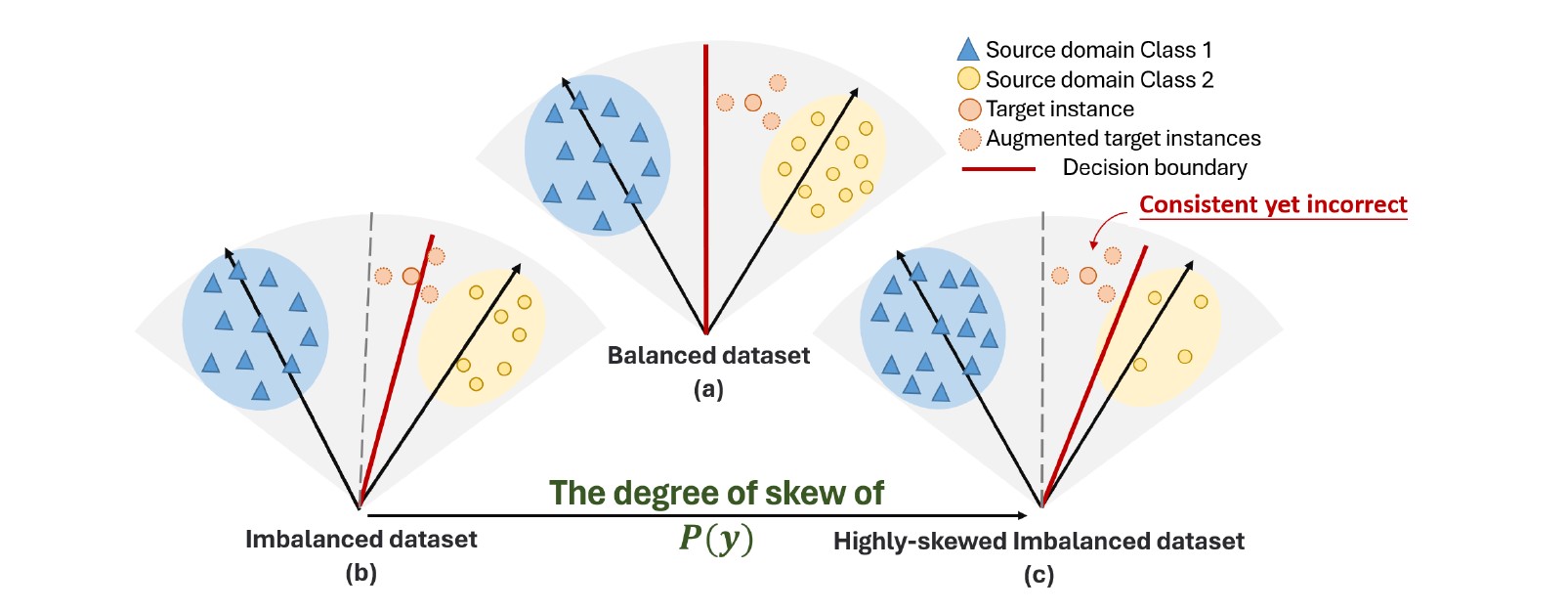
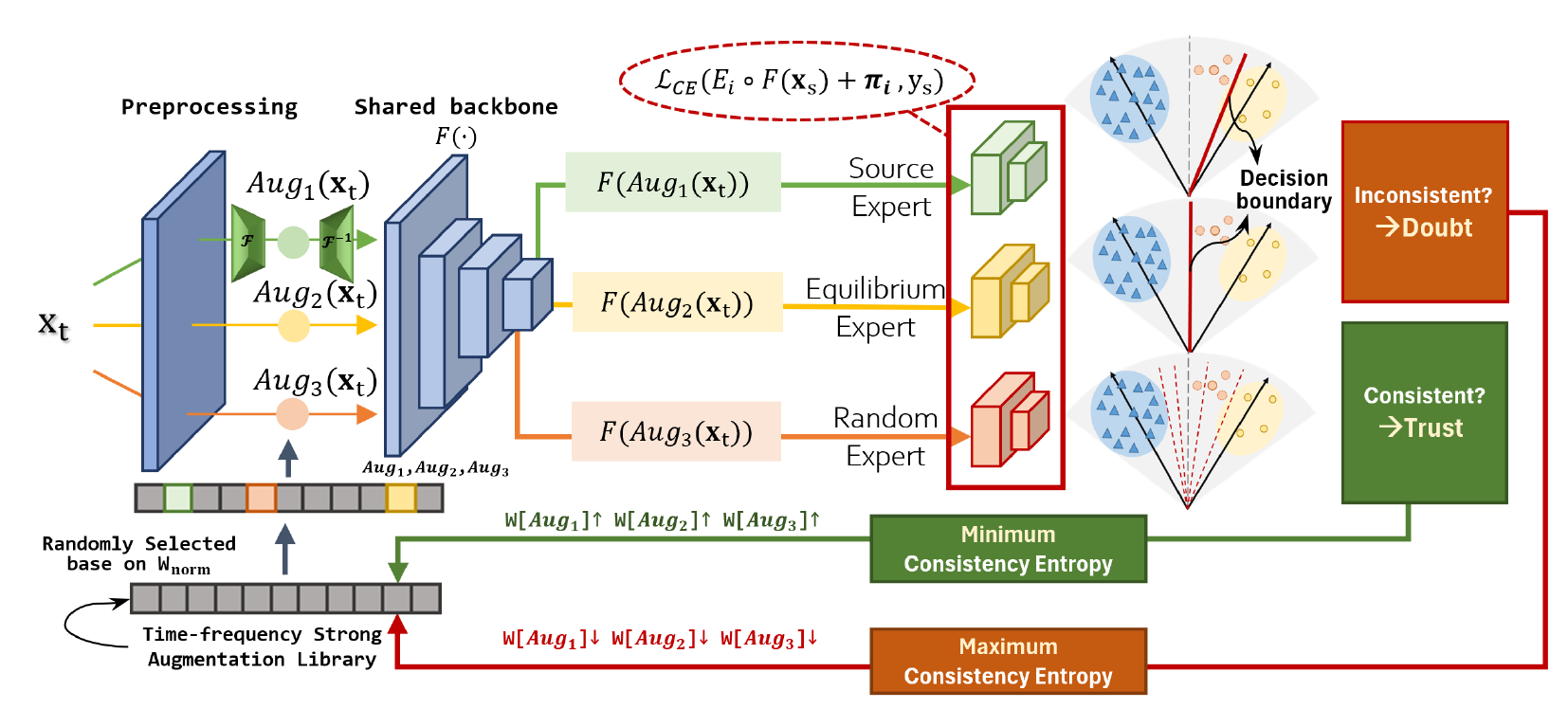
In this paper, we propose a Multi-Expert Consistency Entropy Minimization (MECEM) method for class-imbalanced domain adaptation. Through the incorporation of a multi-expert committee mechanism, we recalibrate decision boundaries in response to imbalanced source distributions, thereby mitigating bias towards minority classes and promoting fairness in committee decisions. Furthermore, we introduce a time-frequency dynamic augmentation mechanism, which simultaneously addresses domain shift on the target domain and dynamically adapts the augmentation library for the classification task. The MECEM method facilitates the propagation of consistency entropy during backpropagation, conveying both the reliability of pseudo-labels and the classification task relevance of augmentation techniques.
Recommended citation: Y. Ma et al., "Class-imbalanced Time Series Adaptation via Multi-Expert Consistency Entropy Minimization," 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Lisbon, Portugal, 2024, pp. 2284-2290, doi: 10.1109/BIBM62325.2024.10822753.
Download Paper
