DDIR: Domain-Disentangled Invariant Representation Learning for Tailored Predictions
Published in Knowledge-Based Systems, 2025
Traditional training methods often struggle to scale effectively with large datasets due to significant distributional differences. Domain generalization (DG) aims to address the challenge of generalizing across multiple-source domains and improving performance in unknown target domains. While many DG methods, such as domain-invariant representation (DIR) learning, excel in handling significant distribution shifts, they often sacrifice performance on in-distribution (IID) data. This trade-off is crucial in real-world applications with uncertain distribution shifts, spanning both out-of-distribution (OOD) and IID scenarios.
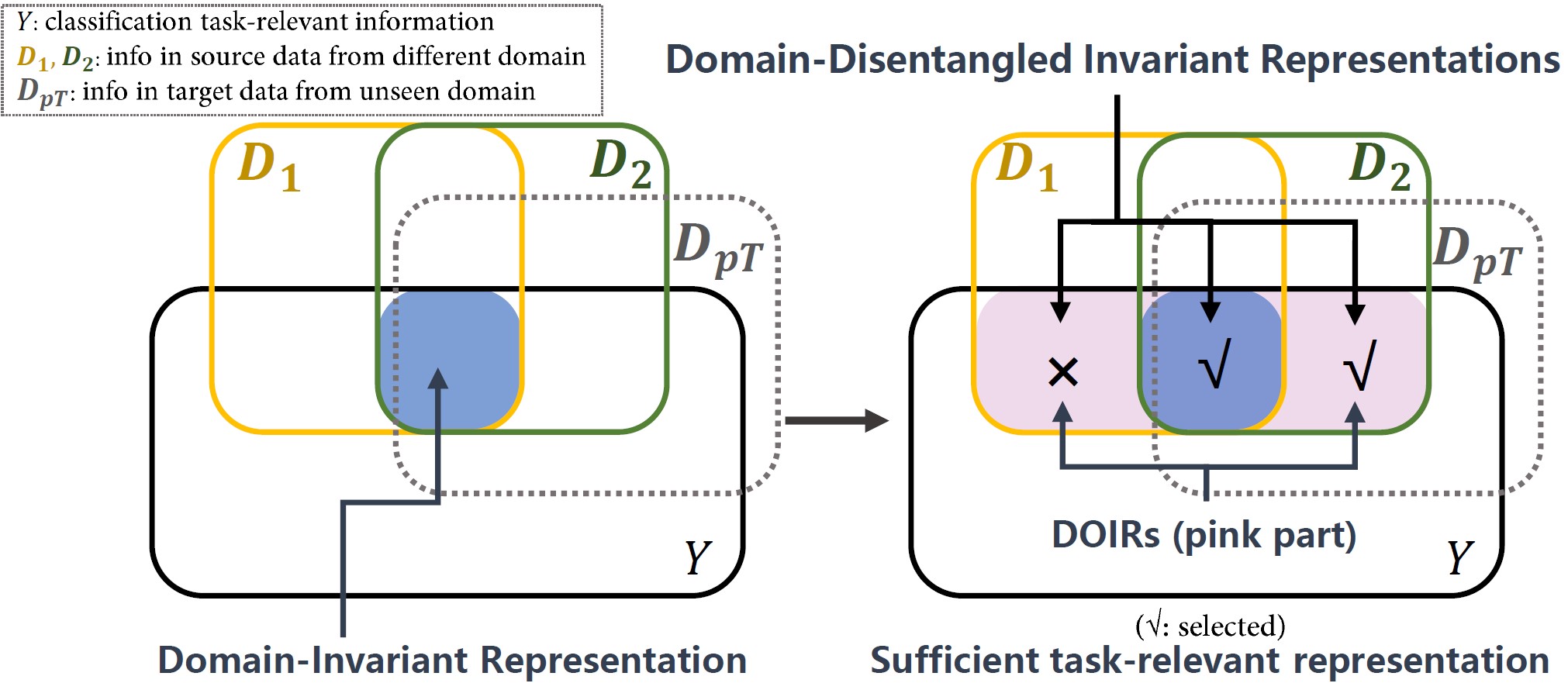
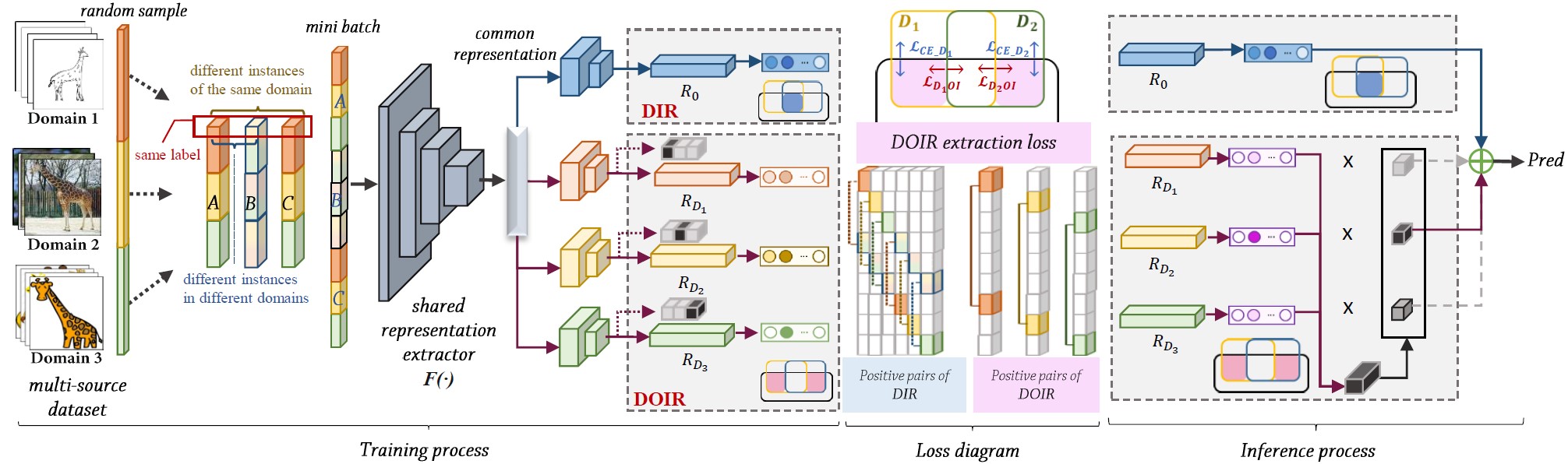
To address this, we identify DIR’s limitation in neglecting task-relevant non-domain-invariant information, termed Domain-Orthogonal Invariant (DOI) information. We propose the Domain-Disentangled Invariant Representation (DDIR) learning, which retains DOI information without introducing redundancy. Our method introduces an information disentanglement loss to extract domain-invariant and different DOI information within a single backbone, achieving lower spatial complexity. Moreover, during inference, we propose optimal DOI selection approaches for individual target samples to avoid utilizing redundant DOI information, enabling tailored predictions for each target sample. Experiments demonstrate DDIR’s effectiveness in enhancing generalization performance across IID and OOD scenarios.
An overall pipeline of the proposed Domain-Disentangled Invariant Representation learning framework.
Resources
🔗 GitHub Repository
📄 Paper Link
Recommended citation: Y. Ma et al., "DDIR: Domain-Disentangled Invariant Representation Learning for Tailored Predictions," in Knowledge-Based Systems 2025.
Download Paper
